left basal ganglia stroke
 Basal ganglia stroke
Basal ganglia strokeBasal Ganglia Stroke What is the basal ganglion coup? Your brain has many parts that work together to control thoughts, actions, answers and everything that happens in your body. Basal nodes are deep neurons in the brain that are key to movement, perception, and judgment. Neurons are brain cells that act as messengers by sending signals through the nervous system. Any injury to the basal nodes may have serious, potentially long-term effects on your movement, perception or judgment. One that interrupts your basal node may cause problems with muscle control or your sense of touch. You could experience. Symptoms of a stroke in the basal node will be similar to others in the . A stroke is the interruption of blood flow to a part of the brain, either because an artery is blocked or because a blood vessel breaks, causing the blood to spill into the nearby brain tissue. Typical symptoms of stroke may include: Due to the unique nature of the basal nodes, symptoms of basal ganglia stroke may also include: Depending on which side of the basal nodes are affected, a variety of other symptoms may arise. For example, if the stroke occurs on the right side of your basal node, you may have difficulty turning left. You may not even know that things happen immediately to your left. A stroke on the right side of your basal node can lead to severe and . Many of the strokes that occur in the basal nodes are . A hemorrhagic stroke occurs when an artery in part of the brain ruptures. This can happen if the wall of an artery becomes so weak that it tears and allows the blood to escape. The blood vessels of the basal nodes are especially small and vulnerable to rupture or rupture. That's why basal gangl strokes are often hemorrhagic strokes as well. All blows are hemorrhagic blows. One can also affect the basal nodes. This occurs when narrow or narrow arteries prevent sufficient blood flow through blood vessels. This tissue of oxygen hunger and nutrients transported in the bloodstream. An ischemic stroke can affect the basal nodes if the , an important blood vessel in the center of the brain, has a clot. Risk factors for hemorrhagic stroke in basal nodes include: These same risk factors can also increase the risk of an ischemic brain attack. When you are in the hospital, your doctor will want to know your symptoms and when they started, as well as your medical history. Some questions you may ask include: Your doctor will also want pictures of your brain to see what is happening. A and analysis can provide detailed images of your brain and blood vessels. Once the emergency staff know what kind of spill they are having, they can give you the right type of treatment. One of the most important aspects of time. The sooner you get to a hospital, preferably to a traction center, the more likely your doctor can minimize the damage caused by the stroke. Call your local emergency services or have someone near you call as soon as you begin. If you are having an ischemic stroke and you arrive at the hospital within 4.5 hours of the onset of symptoms, you may receive a medication that abuses clot called. This can help dissolve most clots. A can be done now within 24 hours of the onset of symptoms. These were established by the American Heart Association (AHA) and American Stroke Association (ASA) in 2018. If you are having a hemorrhagic attack, you cannot take TPA because it inhibits coagulation and increases blood flow. The drug could cause a dangerous episode and potentially more brain damage. For a hemorrhagic blow, surgery may be needed if the break is significant. If you've had a stroke, you must participate in the rehabilitation of strokes. If your balance was affected by stroke, rehabilitation specialists can help you learn to walk again. can help you if your ability to speak was affected. Through rehabilitation, you will also learn exercises and exercises you can do at home to improve your . In the case of a basal ganglion attack, recovery can be especially complicated. A stroke on the right side can make it difficult to perceive sensations on the left side even after the stroke is over. You may have difficulty knowing where your left hand or foot is in space. Making simple movements can be more difficult. In addition to visual difficulties and other physical problems, you can also have emotional problems. You could become more emotional than you were before the basal ganglia attack. It can also become. A mental health professional can help you treat these conditions by combining therapy and medication. Its short- and long-term perspective after a basal ganglion coup depends on how quickly it was treated and how many neurons were lost. The brain can sometimes recover from the injury, but it will take time. Be patient and work closely with your health care team to take action towards recovery. A basal ganglion stroke could have lasting effects that can interfere with their quality of life. Having any type of stroke increases the risk of having another stroke. Having a stroke of basal ganglia or other damage to that part of the brain can also develop. If you join your rehabilitation program and take advantage of services in your community, you may be able to improve your chances of recovery. Acting quickly is the key to responding to strokes, so it is important to recognize some of the most obvious symptoms of strokes. He suggests remembering the acronym ", which means: Do not try to drive you to the hospital if you suspect you are having a stroke. Call an ambulance. Let paramedics evaluate your symptoms and provide initial attention. Last medical review on June 5, 2018
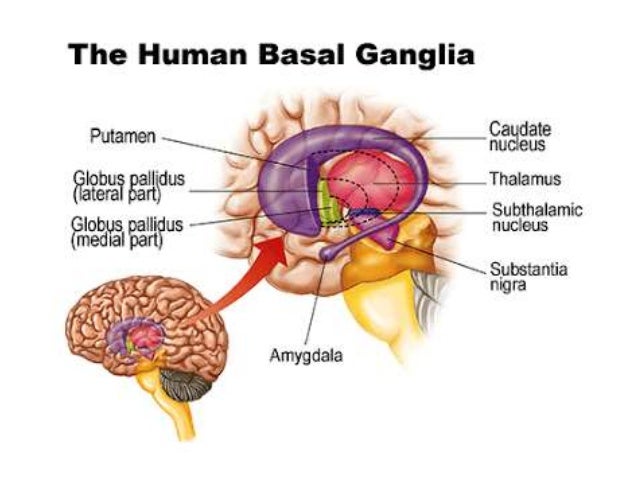
Basal ganglia stroke

Basal Ganglia Stroke: Causes & Symptoms | Study.com

Basal ganglia stroke

Basal ganglia stroke: major Symptoms, causes, and treatment – Knowledgist9
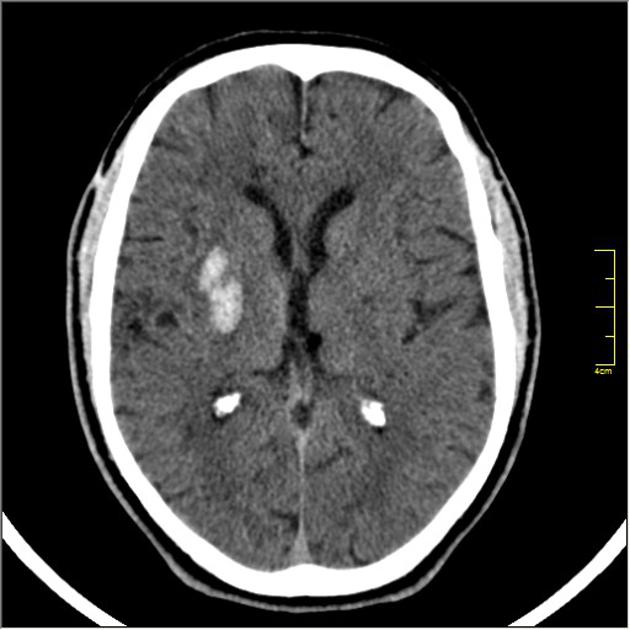
Hemorrhagic stroke - right basal ganglia | Radiology Case | Radiopaedia.org
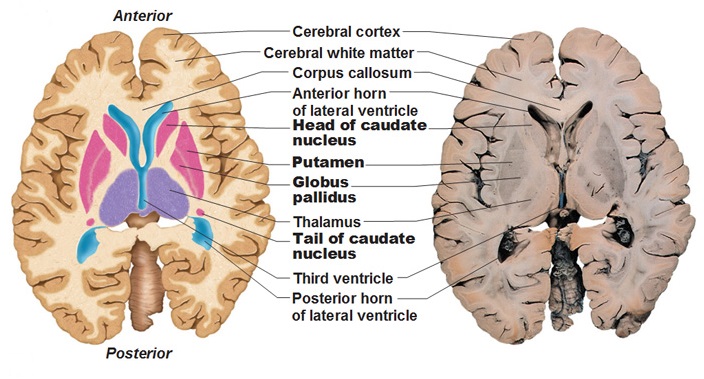
Stroke Medicine for Stroke Physicians and Neurologists

Basal ganglia stroke
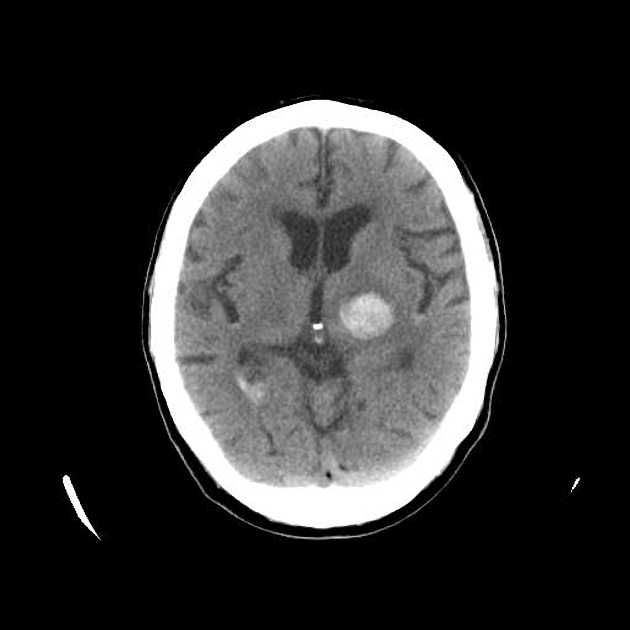
Hemorrhagic stroke: basal ganglia (teaching) | Radiology Case | Radiopaedia.org

10 Neuroscience ideas | basal ganglia, stroke symptoms, brain tissue

Science Source Stock Photos & Video - CT of Basal Ganglia Infarct (Stroke)

Basal ganglia stroke: Symptoms, causes, and treatment

Basal ganglion stroke presenting as subtle behavioural change | BMJ Case Reports

Basal ganglia stroke
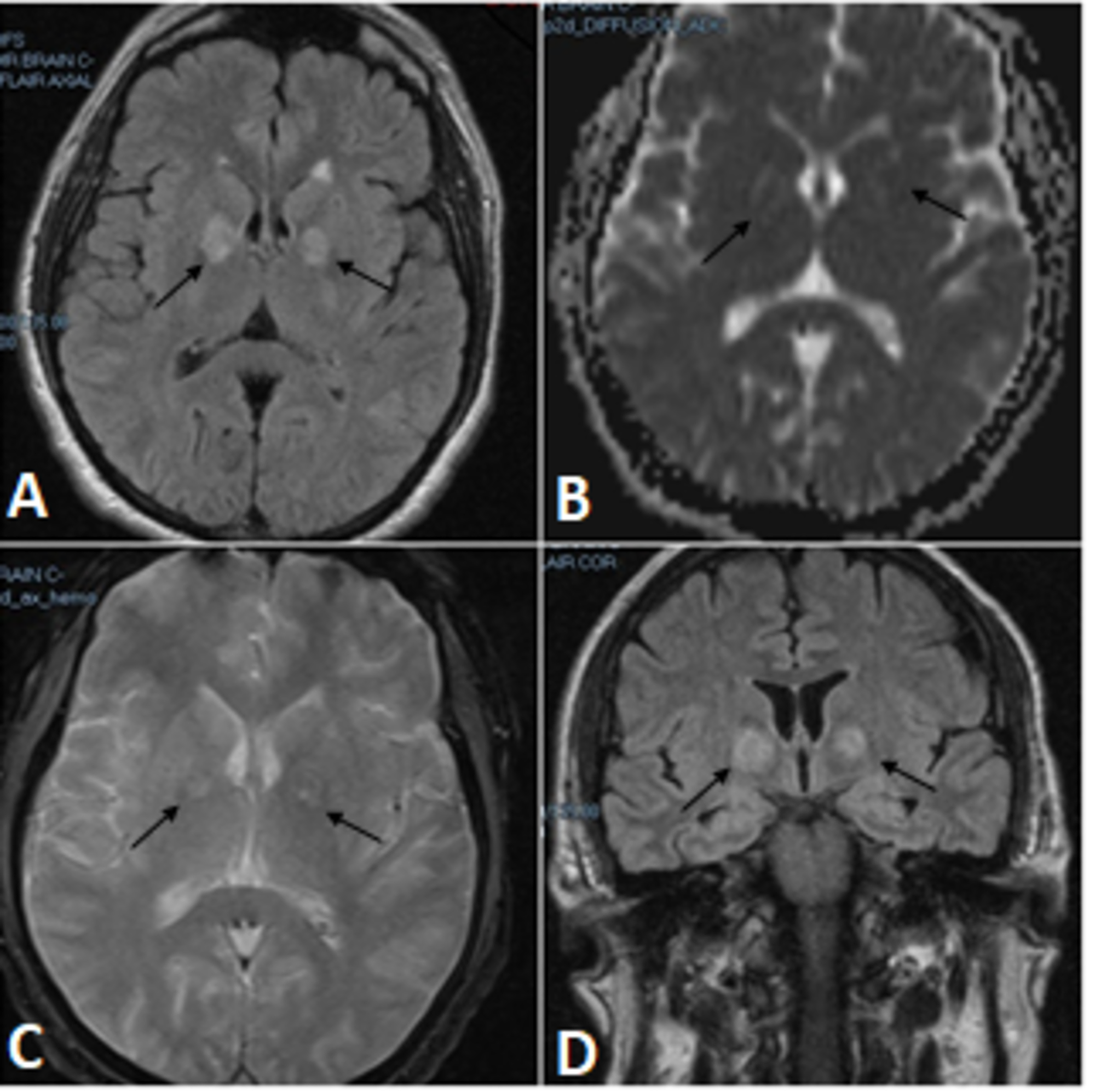
Cureus | Bilateral Basal Ganglia Infarction After Intranasal Use of Cocaine: A Case Report

Deep Basal Ganglia and Capsule
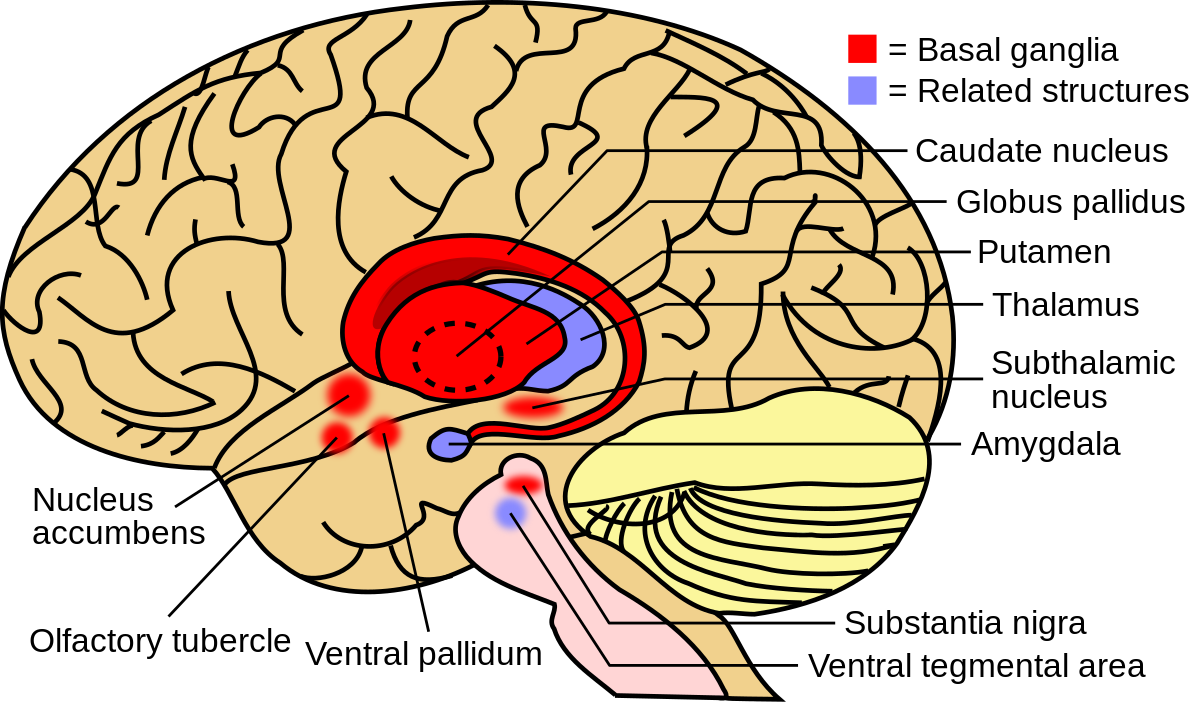
Basal ganglia - Wikipedia

Hoarding In a Patient After Silent Stroke to Left Basal Ganglia - The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry
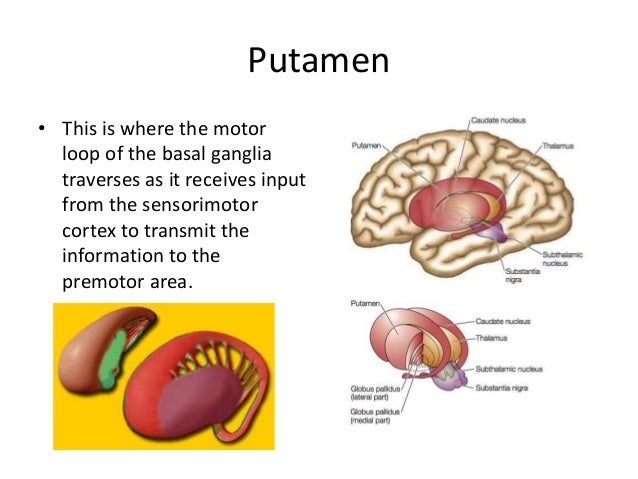
Basal ganglia stroke
Intracerebral Hemorrhage | Internet Stroke Center
Early Basal Ganglia Hyperperfusion on CT Perfusion in Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Marker of Irreversible Damage? | American Journal of Neuroradiology
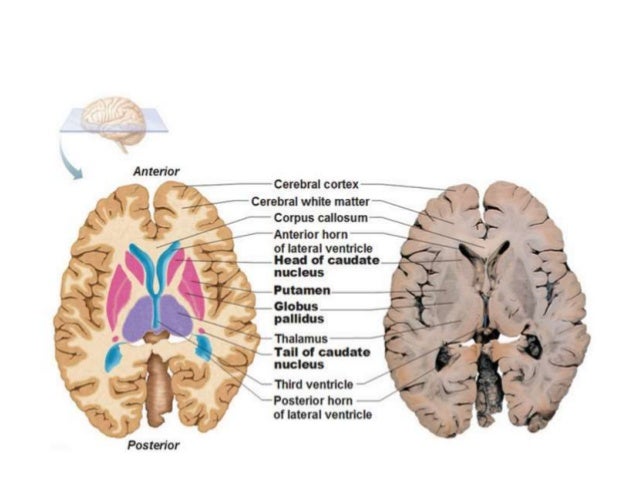
Basal ganglia stroke
Deep Basal Ganglia and Capsule2a

Stroke Medicine for Stroke Physicians and Neurologists

Intracranial Hemorrhage and Neuro Findings | Basal ganglia, Brain hemorrhage, Basal ganglia stroke

Basal Ganglia Stroke: Symptoms, Recovery, and More
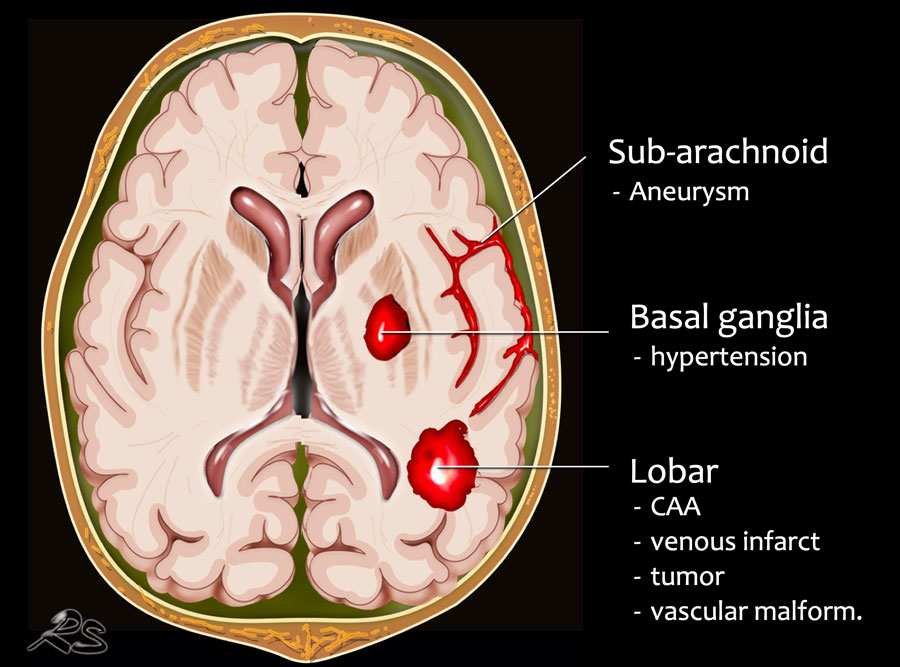
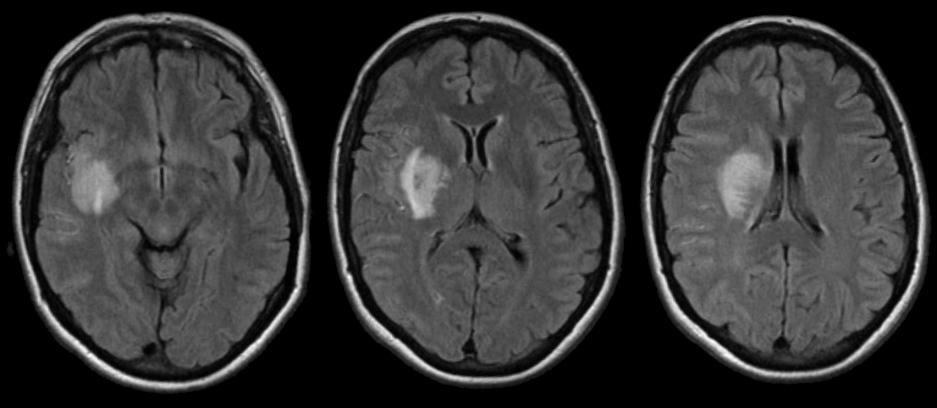
The Radiology Assistant : Non-traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage

FC differences in networks between patients with basal ganglia stroke... | Download Scientific Diagram

Basal ganglia infarct following trivial trauma in a child: Case report and review of literature Munjal S, Srivastava A, Kapoor K, Mehta VS - J Pediatr Neurosci

Basal ganglia stroke

What are basal ganglia stroke symptoms? Causes and treatment

Basal Ganglia Cva symptoms
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13947/Basal_ganglia.png)
Basal ganglia: Gross anatomy and function | Kenhub
Basal Ganglia2

Basal Ganglion Hemorrhage - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics

10 Neuroscience ideas | basal ganglia, stroke symptoms, brain tissue

Loss of basal ganglia (lentiform nucleus) sign. (a) Initial NCCT done 2... | Download Scientific Diagram
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13955/Connections_of_basal_ganglia_-_hyperdirect_pathway.jpg)
Basal ganglia: Gross anatomy and function | Kenhub
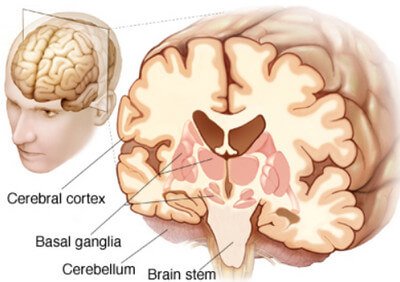
Basal Ganglia - Anatomy, Function, Stroke and Disorders
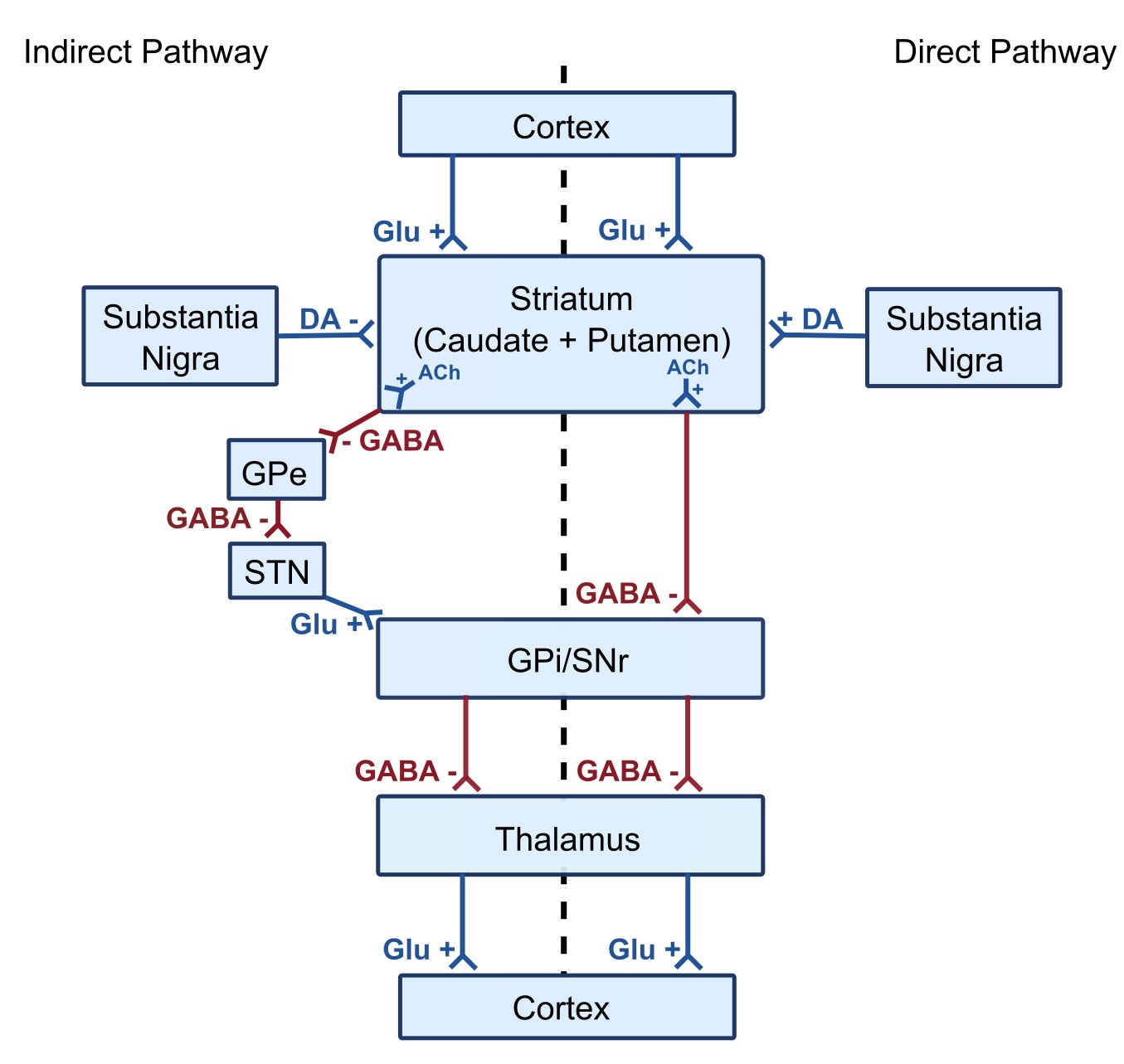
Stroke Medicine for Stroke Physicians and Neurologists
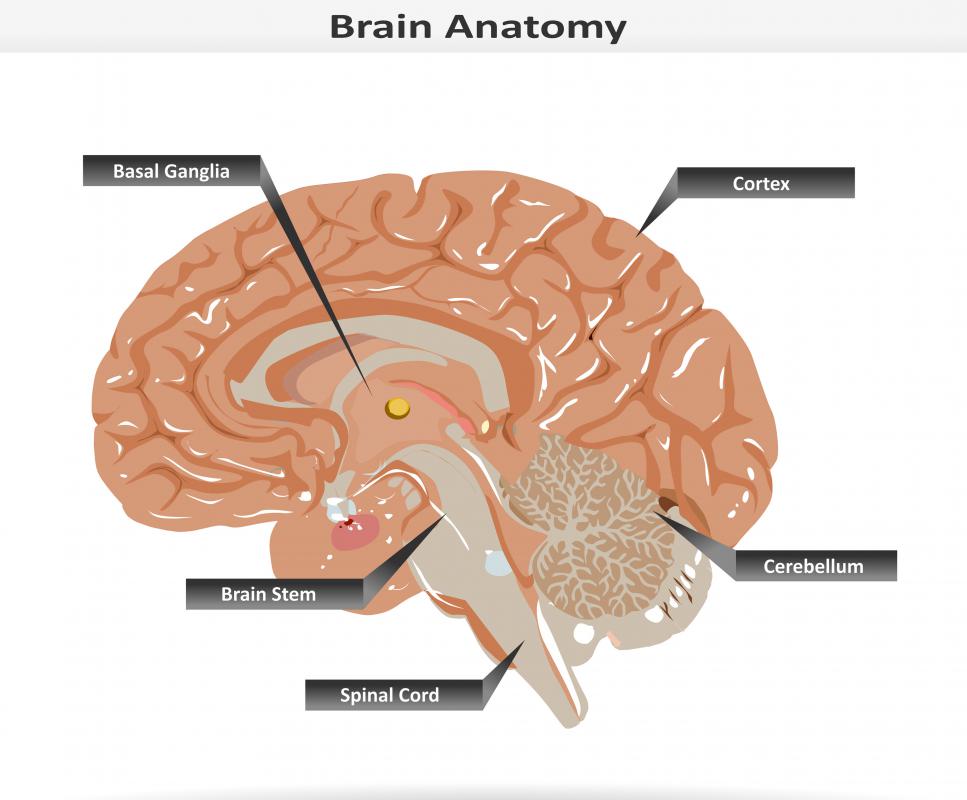
What Is Basal Ganglia Infarction? (with pictures)
Posting Komentar untuk "left basal ganglia stroke"