How Does Down Syndrome Affect The Brain
How does down syndrome affect the brain. Babies with Down syndrome develop much as typical children do but at a somewhat slower rate. Alzheimers disease leads to mood swings speech problems poor memory and confusion. UPDATES ALSO LOOKING AT THE CAUSE OF MICROENCEPHALY SMALL BRAIN.
There is clear evidence that Down syndrome is associated with particularly poor verbal short-term memory performance and a deficit in verbal short-term memory would be expected to negatively affect aspects of language acquisition particularly vocabulary development. Typically in Down Syndrome the brain development in-utero is where most all of the damage occurs. BRAIN DEVELOPMENT IN DOWN SYNDROME.
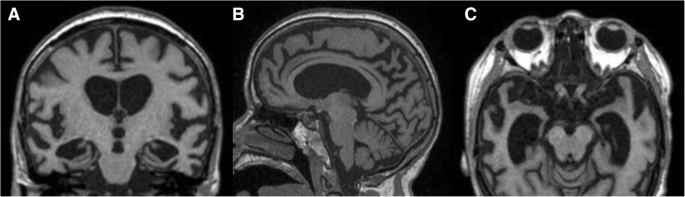
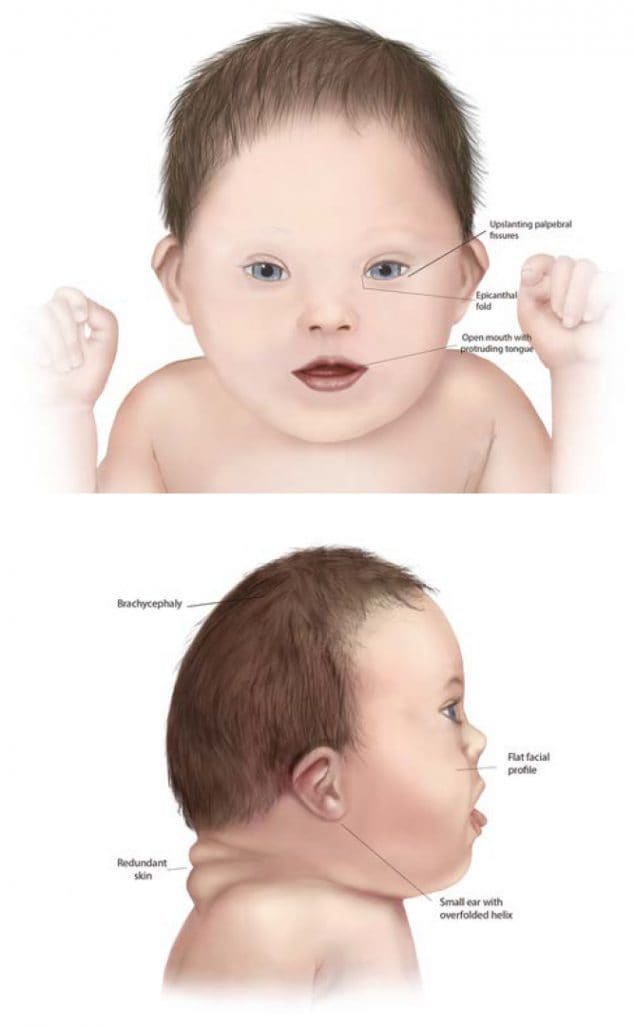
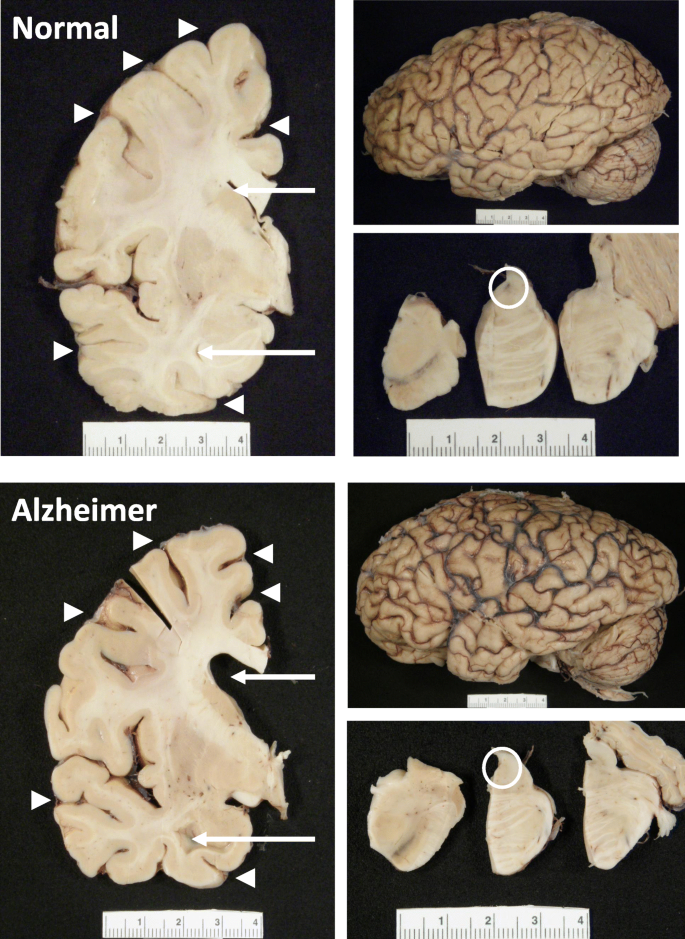
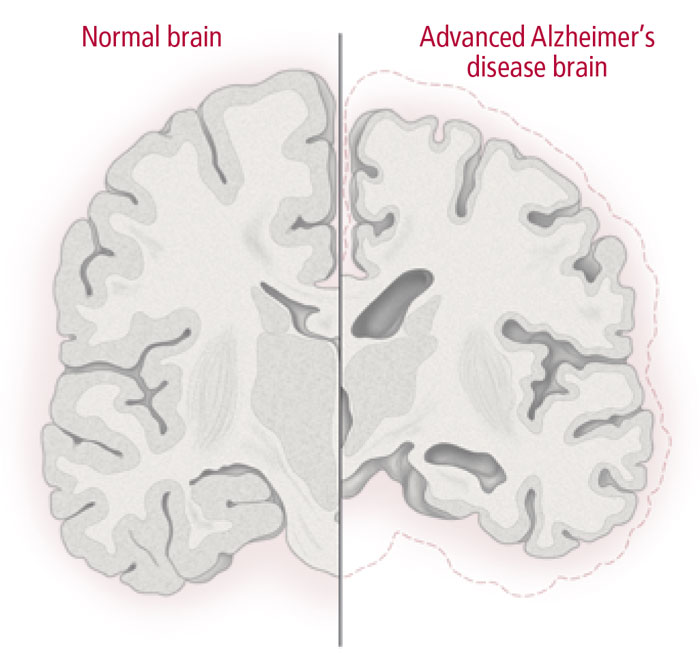
Children with Down syndrome can attend mainstream schools. By age 40 nearly all people with Down syndrome show some neurological changes similar to those seen in Alzheimers disease and most show cognitive decline by age 60. The brain of a child with Down syndrome develops differently from a normal one attaining a form reduced in size and altered in configuration.
Just as their peers do they learn to sit walk talk and toilet train. The phenotype of DS is thought to result from overexpression of a gene s located on the triplicated chromosome region. Speech delays and slow development of fine motor skills are also key characteristics.
Given that adults with Down Syndrome show accelerated volume loss even in the absence of dementia Beacher et al 2010 Haier et al 2008 Teipel et al 2004 these findings may suggest a pattern of volume loss in brain regions relevant to the markedly accelerated onset of Alzheimer Disease in Down Syndrome. Skills such as sitting standing and walking take longer to develop. Most babies and young children with Down syndrome can and do attend childcare centres playgroups and preschool settings.
Recent research may be the forerunner to a range of new treatments for those with small brains aka microencephaly. Individuals with Down syndrome have brains which are on average smaller than those of their non affected counterparts. Down syndrome DS is the most common example of a neurogenetic aneuploid disorder leading to mental retardation.
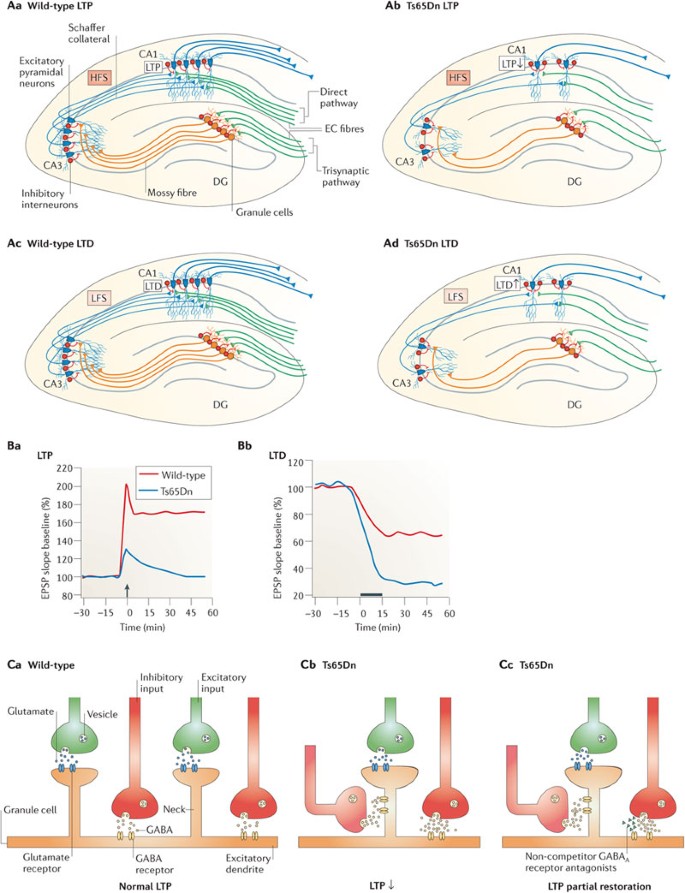
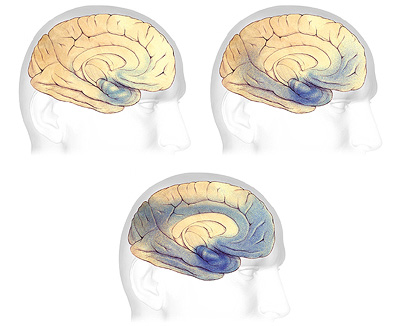
In most cases DS results from an extra copy of human chromosome 21 producing deregulated gene expression in brain that gives raise to subnormal intellectual functioning. Hippocampus is the area of the brain responsible for memory and learning.
Those with Down syndrome are normally more likely to develop dementia particularly the form of dementia known as Alzheimers disease.
In most cases DS results from an extra copy of human chromosome 21 producing deregulated gene expression in brain that gives raise to subnormal intellectual functioning. Those with Down syndrome are normally more likely to develop dementia particularly the form of dementia known as Alzheimers disease. Writing in Nature Medicine Californian researchers found that the extra. Typically in Down Syndrome the brain development in-utero is where most all of the damage occurs. Many students with Down syndrome reach Year 12 and go on to post-school training or tertiary education. By age 40 nearly all people with Down syndrome show some neurological changes similar to those seen in Alzheimers disease and most show cognitive decline by age 60. The brain of a child with Down syndrome develops differently from a normal one attaining a form reduced in size and altered in configuration. Researchers have also discovered differences in their hippocampuses and cerebellum. A lack of a protein in Downs syndrome brains could be the cause of learning and memory problems says a US study.
Normally memory function short and long-term and learning ability is made possible in the hippocampus structure of the brain. Down syndrome DS is the most significant genetic disorder with mental retardation and is caused by trisomy 21. Alzheimers disease leads to mood swings speech problems poor memory and confusion. The brain of a child with Down syndrome develops differently from a normal one attaining a form reduced in size and altered in configuration. BRAIN DEVELOPMENT IN DOWN SYNDROME. UPDATES ALSO LOOKING AT THE CAUSE OF MICROENCEPHALY SMALL BRAIN. Researchers have also discovered differences in their hippocampuses and cerebellum.

/down-syndrome-symptoms-5b48ed4c46e0fb0054c53622.png)








:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/treatment-of-down-syndrome-1120461-v1-deadca996c71459ea361567811088bf8.jpg)














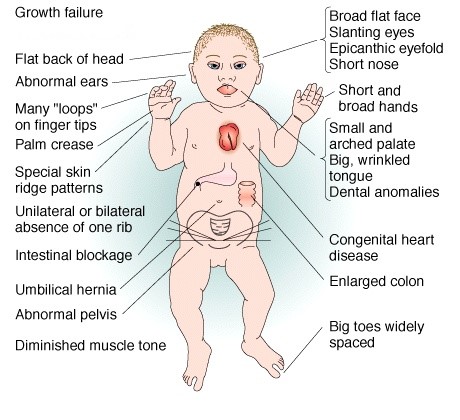


Posting Komentar untuk "How Does Down Syndrome Affect The Brain"